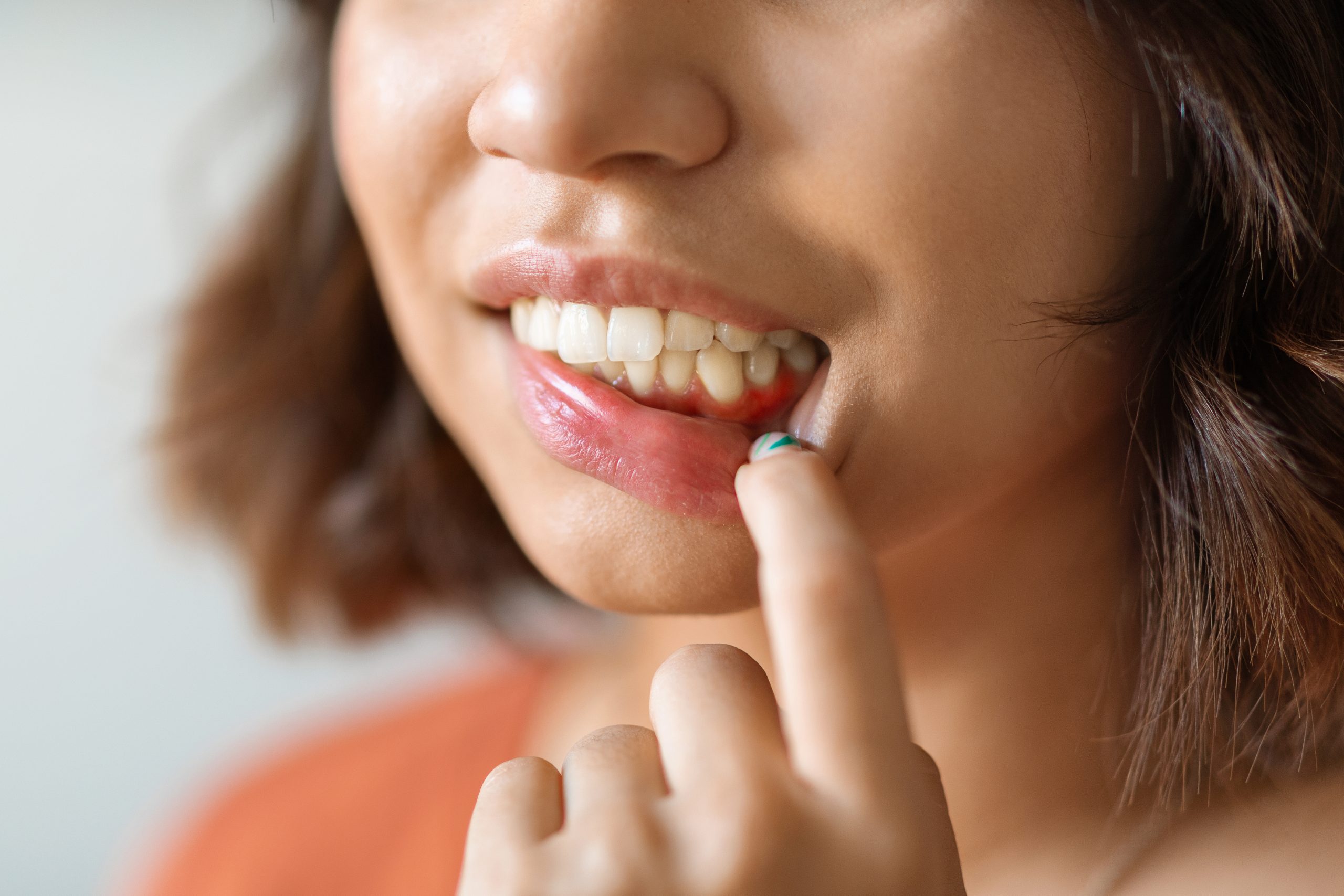
Have you ever looked in the mirror and felt like your teeth appear a little longer than they used to? This common observation is often the first sign of gum recession, a condition where the gum tissue surrounding your teeth begins to pull back or wear away. While it can sound alarming, it’s a gradual process and, with the right dental care, it’s highly manageable.
At The Little Green Building, we believe in empowering our patients with knowledge. This guide will walk you through the most common questions about receding gums, helping you understand the causes, symptoms, and treatments.
What is Gum Recession?
Simply put, gum recession is the reduction in the amount of gum tissue around a tooth, which results in exposing the tooth’s root. This is why teeth can start to look elongated; it’s not that the teeth are growing, but that the gum line is moving, revealing more of the tooth’s structure. This exposed root surface is softer than enamel and more vulnerable to tooth decay, which is why addressing gum loss is so important for your long-term oral health.
How to Know If Your Gums Are Receding?
Besides the visible change in your gum line, one of the most common symptoms is increased tooth sensitivity. The roots of your teeth aren’t covered by hard enamel; they’re meant to be protected by your gums. When exposed, they can become sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks. However, not everyone experiences sensitivity, so regular dental appointments for a professional dental assessment are key for early detection.
During a dental cleaning, your dental hygienist will check your pocket depth, meaning the space between your tooth and gum. Healthy pockets are small, but in cases of gum disease, they can deepen, becoming periodontal pockets that are a clear sign of trouble.
Why Are My Gums Receding? What Causes Gingival Recession?
There isn’t a single cause for gum recession; it’s often a combination of factors. Understanding them is the first step in creating a treatment plan with your dental professional.
- Genetics and Thin Gums: In many cases, it’s hereditary. Some people are simply born with thinner, more delicate gum tissue that is more susceptible to receding.
- Periodontal Disease: This is a major culprit. Poor dental hygiene allows dental plaque to build up, leading to gum inflammation (gingivitis). If left untreated, this can progress to periodontal disease, where the gums pull away from the teeth. Symptoms often include bleeding gums. In severe cases, known as advanced periodontitis, it can lead to jawbone loss and eventual tooth loss. There is even a known link between severe periodontal disease and heart disease.
- Aggressive Tooth Brushing: It might seem like you’re doing a good thing, but scrubbing your teeth too hard, especially with hard-bristled toothbrushes, can physically wear away your gum tissue.
- Trauma or Injury: A direct injury to a tooth can cause the surrounding gum to recede.
- Orthodontic Treatment: The movement of teeth during treatments like braces can sometimes contribute to recession.
- Medical Procedures: Procedures like root canals can sometimes affect the health of the surrounding gum tissue.
- Lifestyle Factors: Habits like tobacco use are strongly linked to various gum problems, including recession.
How to Stop Receding Gums?
This is a crucial question. Unfortunately, you can’t completely stop the process of recession once it has begun. The goal of treatment is to slow it down significantly and prevent further damage. The best way to do this is through a proactive oral hygiene routine and regular professional care. This includes:
- Proper Oral Hygiene Techniques: Your dental team can show you the best way to brush and floss gently but effectively.
- Using the Right Tools: Switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush is a must.
- Regular Dental Cleanings: A deep cleaning, also known as tooth scaling or scaling and root planing, is essential for removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line.
Can Flossing Cause Gum Recession?
No, not when done correctly. In fact, flossing is vital for removing plaque between the teeth and preventing the gum disease that leads to recession. However, if someone is abusing the floss by snapping it down hard and hurting the gums, that repeated trauma could potentially contribute to recession.
Can Gums Grow Back?
Once gum tissue is lost, it does not naturally grow back. The body cannot regenerate this type of tissue. This is why prevention and slowing the progression are so important. While the gum itself won’t regrow, there are highly effective surgical treatments that can replace the missing tissue.
What is the Treatment for Gingival Recession?
Your treatment plan will depend on the severity of the recession. For mild cases, the focus is on maintenance. This includes excellent oral hygiene, regular cleanings, and sometimes using desensitizing agents like a desensitizing toothpaste containing potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride. For minor aesthetic concerns, a dentist might use dental bonding with a tooth-colored composite resin (a composite restoration) to cover the exposed root. Your dentist may also recommend a special antibacterial mouthwash containing chlorhexidine digluconate, such as Corsodyl 0.2% Mouthwash, for a short period to control bacteria.
In more extreme cases where a significant amount of gum has been lost, a dental surgeon may recommend a surgical procedure. The most common is gum grafting (or a gingival graft).
- Gum Grafting Procedures: The goal is to achieve root coverage with a soft tissue graft. This involves taking graft tissue, usually from the roof of your mouth, and stitching it into place over the receded area. There are several types, including a connective tissue graft, free gingival graft, or a pedicle graft. Other advanced techniques include pinhole gum lifting.
- Supporting Procedures: If there has been significant jawbone degeneration, procedures like a bone graft/bone grafting or guided tissue regeneration might be necessary to support the gum tissue and ensure the long-term success of treatments like dental implants. A surgeon might also perform pocket reduction surgery to clean out deep periodontal pockets.
Take Control of Your Gum Health Today
Understanding gum recession is the first step toward protecting your smile for a lifetime. While you can’t turn back the clock on gum loss, you can take decisive action to manage it effectively.
If you’ve noticed your teeth looking longer, are experiencing sensitivity, or are simply due for a check-up, don’t wait. Our friendly and compassionate dental team at The Little Green Building is here to help. We will provide a thorough dental assessment and work with you to create a personalized plan to protect your gums and your overall health.
Book your consultation with us today, and let’s keep your smile bright and healthy for years to come!