A dental issue that goes beyond a simple ache and enters the realm of a true emergency is a tooth abscess. Understanding the signs of an abscessed tooth is crucial for protecting your overall oral health. This blog post will break down what a dental abscess is, how it develops, and why immediate treatment is non-negotiable.
What is a Dental Abscess?
A dental abscess is essentially an acute infection caused by a bacterial infection in the dental area. This infection can affect soft tissues like the gum or cheek, and in more advanced stages, it can cause the face or jaw to become visibly swollen.
There are primarily two types of tooth abscesses:
- Periapical Abscess: This is the most common form, also known as a Dentoalveolar abscess or Odontogenic abscess. It forms at the tip of the tooth’s root.
- Periodontal Abscess: This infection is located in the gum tissue (gingiva) next to the root of a tooth and is often related to advanced gum disease.
Regardless of the type, both conditions indicate a serious breakdown in your immune system’s ability to fight the infection, posing a risk to the surrounding oral tissues and even jawbone tissues.
How Do You Get an Abscessed Tooth?
The vast majority of tooth abscesses are the result of neglecting tooth decay or dental decay.
When a dental cavity is ignored, the decay penetrates the outer layer of tooth enamel (the enamel covering or enamel surface) and reaches the inner, sensitive dental pulp. Once the bacteria reach the pulp, the infection quickly takes hold.
Other ways a tooth can become abscessed include:
- Complications from a Filling: Occasionally, a tooth that has already been filled may develop an infection underneath the restoration.
- Cracked or Chipped Teeth: A physical injury or dental trauma that results in cracked or chipped teeth can create an opening for bacteria to enter the pulp chamber and cause an infection.
- Advanced Gum Infection: Untreated gum disease can lead to a periodontal abscess.
Maintaining good oral hygiene using fluoride toothpaste, dental floss, and interdental brushes, along with regular dental cleanings, are key dental habits that prevent the development of Abscessed
What are the Signs of an abscessed Tooth?
The signs of an abscessed tooth can range from minor discomfort to debilitating pain. Pay close attention to these symptoms:
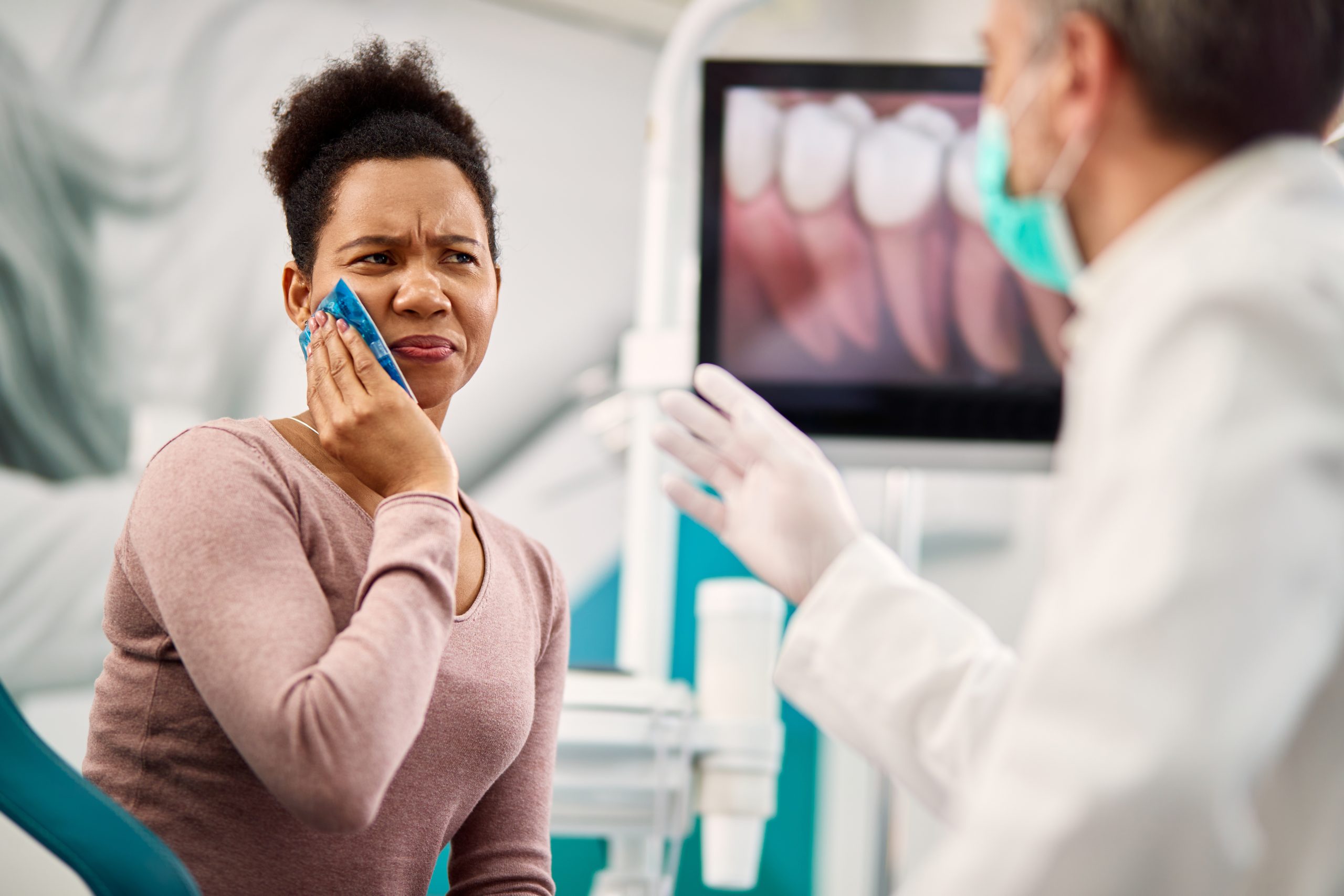
- Severe and Persistent Tooth Pain: This is the most common sign. The tooth pain is often described as throbbing or shooting.
- Swelling: Swelling of the gum near the tooth, which eventually progresses to the cheek or face (swollen face).
- Foul Odor/Taste: A sudden release of a foul odor and unpleasant taste in the mouth can signal that the abscess has ruptured and is draining pus (abscess drainage).
- Temperature Sensitivity: Pain when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks.
- Fever: A general sign that your body is fighting a serious infection.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Tender or swollen lymph nodes in the neck or under the jaw.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) that can’t be resolved with brushing.
Your dental healthcare provider will typically confirm the diagnosis using a visual examination and a dental X-ray, which can show the extent of the infection in the jawbone tissues. Occasionally, a more detailed image, like a CT scan, may be required for complex cases.
Tooth Abscess Treatment: The Urgent Next Steps
Tooth abscess treatment is not optional; it’s an urgent medical necessity. Painkillers are not enough to treat a bacterial infection that requires intervention.
Treatment depends on the stage and severity of the dental condition and typically involves one or more of the following surgical procedures:
- Incision and Drainage (I&D): The dentist performs an incision and drainage to release the accumulated pus, often under a local anaesthetic.
- Root Canal Therapy: For a tooth that can be saved, a root canal treatment is performed. This involves removing the infected dental pulp and sealing the pulp chamber to prevent re-infection. This is the goal when possible.
- Extraction: If the tooth is too damaged to be saved by a root canal, extraction may be necessary. This also ensures the source of the infection is eliminated.
Antibiotics are usually prescribed at this stage to help eliminate the remaining bacterial infection and prevent further spread.
If you cannot see your regular dental clinic or dental healthcare provider immediately, you must go to an Emergency Medicine room in the hospital. This is especially true if you have a high fever, severe swelling, or difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Abscessed Tooth and Swelling Face: When Infection Spreads
Swelling of the face is a major warning sign of an abscessed tooth and indicates the infection is escalating.
This swelling occurs because the bacteria and pus from the infected tooth or pulp chamber have begun to leak out into the surrounding tissues. As this progresses, the infection is no longer contained just within the tooth or gum line. The initial localized swelling of the gum rapidly expands to involve the cheek and potentially the entire side of the face or jaw. This is sometimes referred to as a swollen face in relation to dental pain.
Furthermore, the body’s immune system responds to the spreading bacterial infection by causing swelling of lymph nodes near the jaw and neck. When an abscessed tooth is present, these Lymph Nodes become enlarged and tender, a further sign that the infection is active and spreading via the blood vessels.
If your face is swollen due to an abscess, this is an emergency condition and must be treated as soon as possible.
Why the Urgency? Life-Threatening Complications
The urgency of this situation cannot be overstated. If ignored or the treatment is delayed, a seemingly contained tooth infection might lead to serious or life-threatening complications.
The danger lies in the pus, which travels along blood vessels and the tissue planes of the face and neck. The infection can spread upwards into the head, potentially leading to cavernous sinus thrombosis (a blood clot near the brain), or it could travel downwards into the neck, resulting in severe and dangerous conditions like Ludwig’s angina (a rapidly spreading infection beneath the floor of the mouth) or a parapharyngeal abscess. In rare but catastrophic cases, the pus can lead to an infection that affects the brain or heart.
Don’t Delay: Treat Your Abscess Today!
Don’t wait when facing a potential tooth abscess. As a serious dental emergency, immediate care is critical.
The Little Green Building is here for you. Contact our experienced team right away for urgent assessment and treatment.
Call The Little Green Building (647) 699-3786 today to get the immediate care you need or book our emergency services!